About
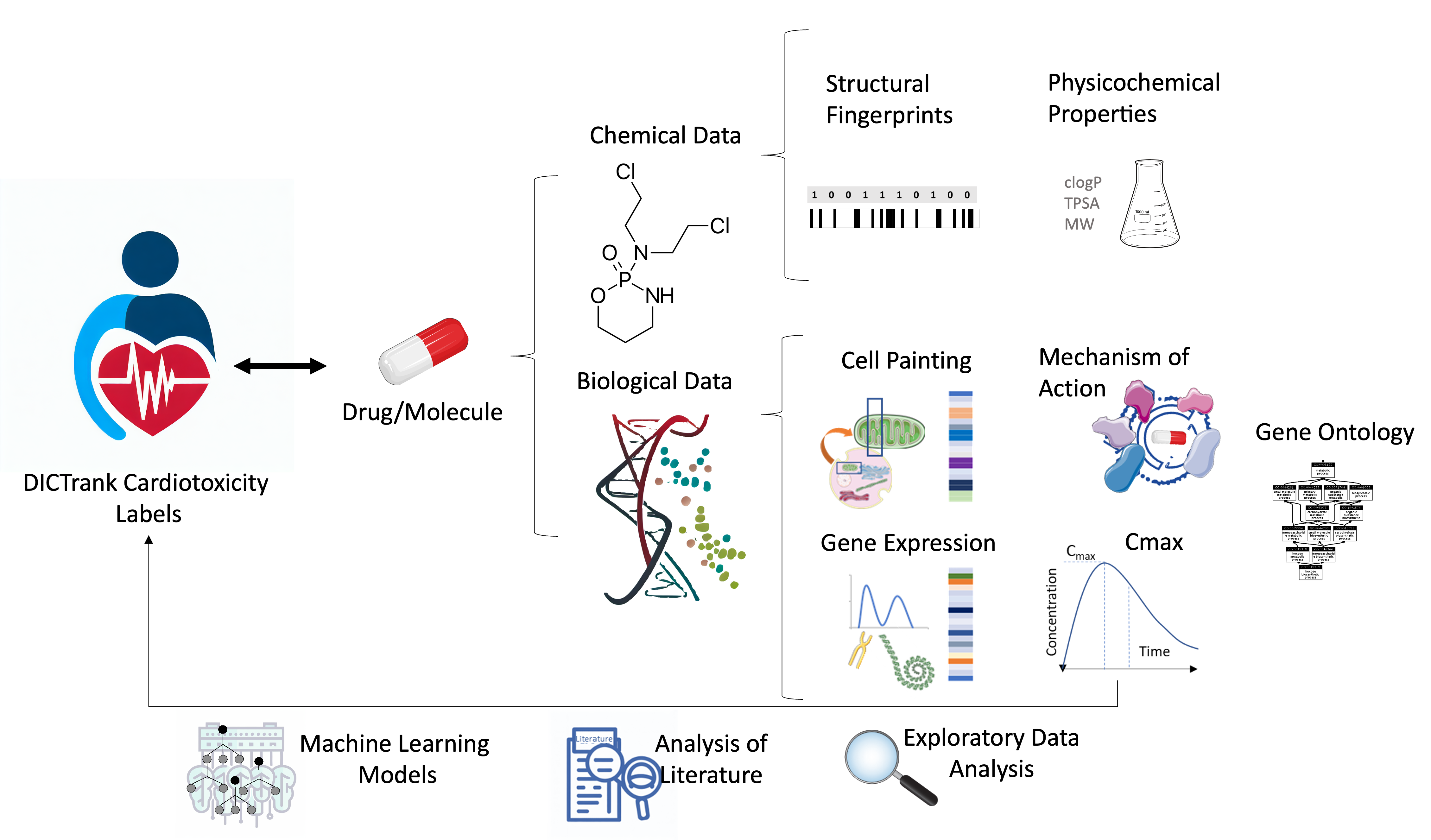
The DICTrank dataset is a novel benchmark for ML in cardiotoxicity and a pivotal advancement for predicting cardiotoxicity as a clinical label, akin to the earlier DILIrank dataset (2016) which is now widely used in drug discovery as a benchmark for clinical data on liver toxicity.
Our work aims at driving insights from chemical and biological data, including physicochemical properties, mechanism of action (MOA), Cell Painting and pharmacokinetic data. Models developed in this study are predictive of DICTrank with high accuracy and all models and datasets are made publicly available.
We show that protein targets, particularly ion channels such as hERG, alongside specific physicochemical attributes like the electrotopological state, are potent indicators of DICT. Within the biological data spectrum, for example, in the Cell Painting assay, we shown that specifically ER stress-related features exhibited significant potential in discerning cardiotoxic compounds. Our analysis underscored the relevance of specific Gene Ontology annotations, especially those related to transport vesicles and potassium ion transmembrane transport, in discerning the compounds that fall into the most-concern DICT category.
For referencing DICTrank, please cite the original paper by US FDA here
For referencing DICTrank Predictor, please cite:
Seal, S, Hosseini-Gerami, L, García-Ortegón, M, Singh, S, Bender, A and Carpenter, AE(2023). Insights into Drug Cardiotoxicity from Biological and Chemical Data: The First Public Classifiers for FDA DICTrank . bioRxiv, 2023.